In the realm of cybersecurity, there's a game that isn't just about fun, but also about learning, challenges, and honing your hacking skills. It's called Capture The Flag (CTF).
In this article, we'll delve into what CTF is, how it works, and why it's a crucial training ground for aspiring cybersecurity professionals.
1. Understanding Capture The Flag (CTF)
Capture The Flag (CTF) is a cybersecurity competition that simulates real-world hacking scenarios. Participants solve puzzles, decode messages, exploit vulnerabilities, and ultimately retrieve hidden "flags" to earn points. Flags are unique strings that prove a challenge's completion.
 |
Image: A visual representation of a CTF flag being captured |
2. Categories of CTF Challenges
CTF challenges are divided into distinct categories, mirroring the diverse aspects of cybersecurity:
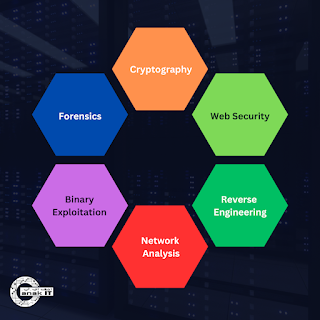 |
| Image: 6 common categories of Cyber Battle: Capture The Flag |
2.1 Cryptography:
Cryptography challenges involve deciphering encoded messages, cracking codes, and understanding encryption techniques. You'll encounter various types of cyphers, substitution methods, and algorithms. Participants often need to apply analytical and mathematical thinking to break the encryption.
2.2 Web Security:
Web security challenges are focused on identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities present in web applications. These challenges mimic real-world scenarios where hackers attempt to bypass security mechanisms, execute code injection, or manipulate URLs to gain unauthorized access.
2.3 Forensics:
Forensics challenges involve analyzing digital artefacts, logs, and files to extract hidden information. Participants may recover deleted files, decipher hidden messages in images, or reverse-engineer malware to understand its behaviour. These challenges test your attention to detail and analytical skills.
2.4 Reverse Engineering:
Reverse engineering challenges require participants to dissect compiled programs or binaries to understand their functionality. You'll explore executable files, disassemble code, and identify vulnerabilities. This category is particularly useful for understanding how malware operates.
2.5 Binary Exploitation:
Binary exploitation challenges involve exploiting vulnerabilities in compiled programs. Participants find ways to manipulate input data to trigger buffer overflows, code execution, or privilege escalation. This category focuses on understanding software vulnerabilities and crafting exploits.
2.6 Network Analysis:
Network analysis challenges focus on analyzing network traffic to uncover vulnerabilities or hidden information. You might examine packet captures, identify potential security flaws, and reconstruct network activities to understand their implications.
3. How Does CTF Work?
3.1 Challenge Discovery
3.2 Problem-Solving
 |
| Image: Cyber Battle participants Source: itpss.com |
- Analyze Code: Examine source code, binaries, or other files for vulnerabilities and hidden information.
- Reverse Engineer: Disassemble and understand the inner workings of compiled programs.
- Decipher: Decode encrypted messages, cyphers, and codes using cryptography principles.
- Examine Artifacts: Analyze digital artefacts like images, logs, or packet captures to extract relevant information.
3.3 Flag Retrieval
3.4 Scoring
| Image: Scoreboard sample of Cyber Battle: Capture The Flag, Source: haxf4rall.com |
4. Importance of CTF Competitions
4.1 Skill Enhancement and Practical Application:
 |
| Image: Participants of the Cyber Battle: Capture The Flag. Source: BruCert instagram |
4.2 Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking:
 |
| Image: Brainstorming session. Source: wework.com |
4.3 Exposure to Diverse Domains:
 |
| Image: Representation of diverse into cybersecurity domains. Source: evelynlim.com |
4.4 Hands-On Learning and Active Participation:
| Image: photo of 2016’s Cyber Battle: Capture The Flag competition, Source: itpss.com |
4.5 Teamwork and Collaboration:
 |
| Image: representing teamwork and collaboration. Source: quietrev.com |
4.6 Competitive Spirit and Motivation:
5. Preparing for CTF Success
5.1 Learn Key Concepts
- Cryptography: Familiarize yourself with encryption algorithms, decryption methods, and common cryptographic attacks.
- Web Security: Understand web vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and request forgery.
- Forensics: Learn techniques to analyze digital artefacts, recover deleted data, and reconstruct events.
- Reverse Engineering: Study assembly language and understand how to reverse-engineer compiled programs.
- Binary Exploitation: Learn about buffer overflows, format string vulnerabilities, and binary analysis.
- Network Analysis: Gain insights into network protocols, packet capture analysis, and network attacks.
5.2 Practice Regularly
- CTF Platforms: Explore CTF platforms like PicoCTF, Hack The Box, TryHackMe and PentesterLab Engage with challenges of varying difficulty levels to improve your skills.
- Wargames: Participate in cybersecurity wargames that simulate real-world scenarios and test your problem-solving abilities.
- Online Tutorials: Follow online tutorials that cover CTF-related topics and provide step-by-step guidance on solving challenges.
5.3 Joining Communities
- CTF Forums: Participate in CTF forums and communities to connect with like-minded individuals, ask questions, and share insights.
- Online Platforms: Join CTF-related Discord servers, Reddit communities, and social media groups to stay updated and interact with experts.
5.4 Team Collaboration
- Team Formation: Consider forming or joining a CTF team. Diverse skills and expertise within a team can enhance problem-solving and strategy development.
- Knowledge Sharing: Collaborate with team members to share insights, solutions, and tactics for tackling challenges effectively.
Stay Updated with Trends
- Cybersecurity News: Follow cybersecurity news, blogs, and websites to stay informed about the latest vulnerabilities, techniques, and trends.
- CTF Write-Ups: Read CTF write-ups and walkthroughs to understand different solution approaches and expand your toolkit.
Embrace the CTF Journey
| Image: Top 3 teams of Cyber Battle: Capture The Flag 2016 Source: itpss.com |
 |
| Image: Reaching the summit. Source: zermatt.ch |




















